ChatGPT Prompt Engineering: 12 Tips Tested and Ranked [2025]
![ChatGPT Prompt Engineering: 12 Tips Tested and Ranked [2025]](https://latetechpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/ChatGPT-Prompt-Engineering-12-Tips-Tested-and-Ranked-2025.webp.webp)
I’ve been obsessed with ChatGPT for the last few years. But there’s one thing all language models lack: consistency.
In the beginning, I would ask for marketing copy and get something either brilliant or completely useless. One day, it would nail my brand voice perfectly. The next day, pure corporate word salad.
And while everyone has their own tips and LinkedIn gurus are selling courses, there are a few fundamentals that continue to work perfectly well.
I tested 12 of the most popular prompt engineering tips using real business scenarios: marketing copy, customer emails, and product descriptions. Here’s what actually moved the needle.
How Did I Test These Techniques?
I’m three real business case scenarios across this guide:
- Product launch emails for a project management app
- Instagram ad copy for a coffee subscription service
- Customer support response to refund requests
I ran each prompt three to five times, just clicking on the try again button, to see what kind of results the prompt generates. My only expectation was for ChatGPT to maintain consistency with the prompt as well as the style.
👉Note: All prompts are tested on the latest ChatGPT 5 model with “Thinking” set to “Auto” and no personalization prompting.
And considering that language models never output the same response twice, it’s unlikely you’ll see the exact output as I show in the screenshot.
Instead of taking these outputs at face value, I recommend paying attention to the output patterns so you can see the differences.
I’ve also added a score on a scale of 10, where 10 is the highest in terms of usability and reliability, and 1 is the lowest.
Let’s get prompting.
1. Be Ridiculously Specific: 10/10
ChatGPT is a simple pattern recognition machine. The language and data in your prompt will define what your output is like. Generally, the difference between generic AI content and usable material is specificity about deliverables, audience, and constraints.
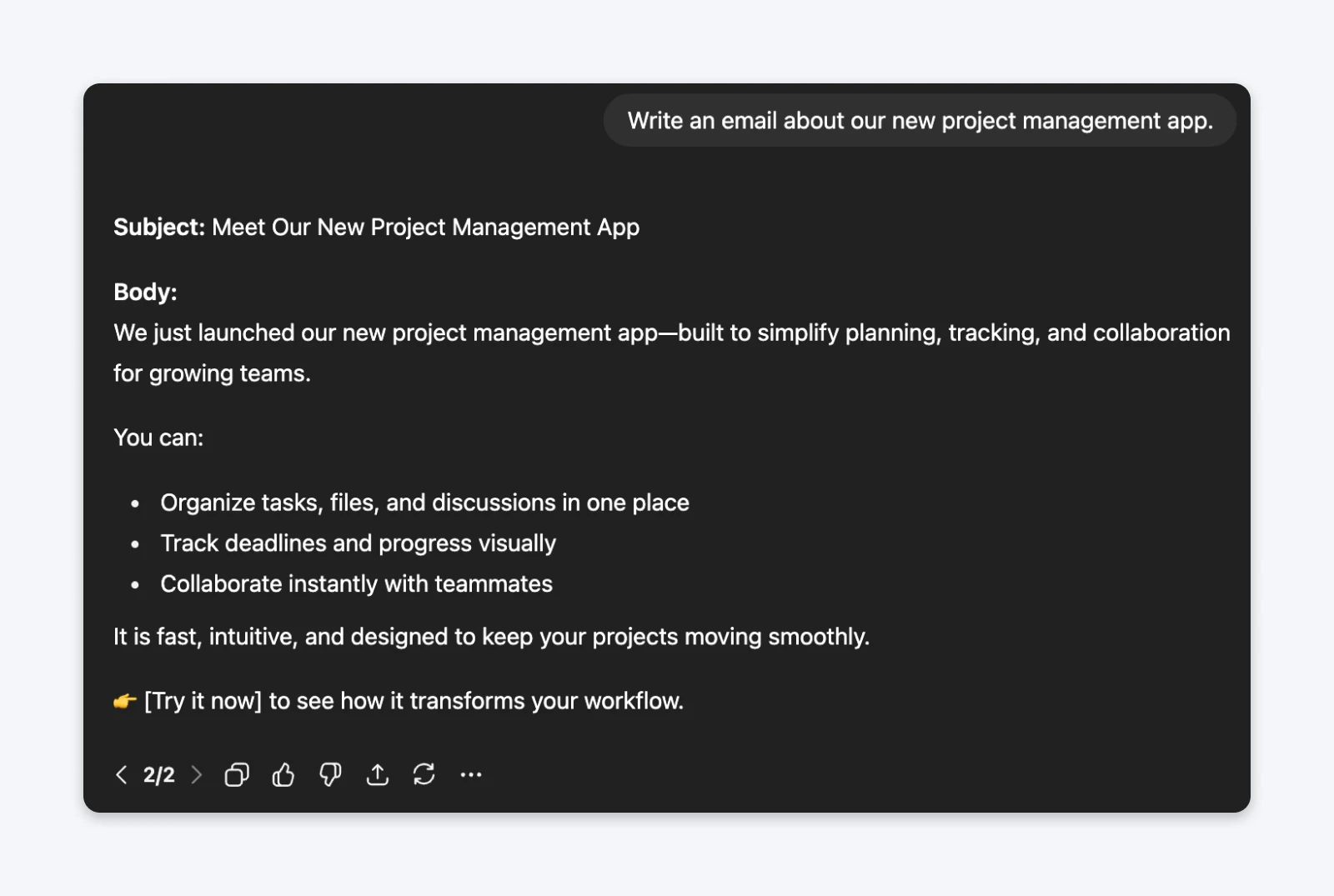
The prompt (vague/basic):Write an email about our new project management app.
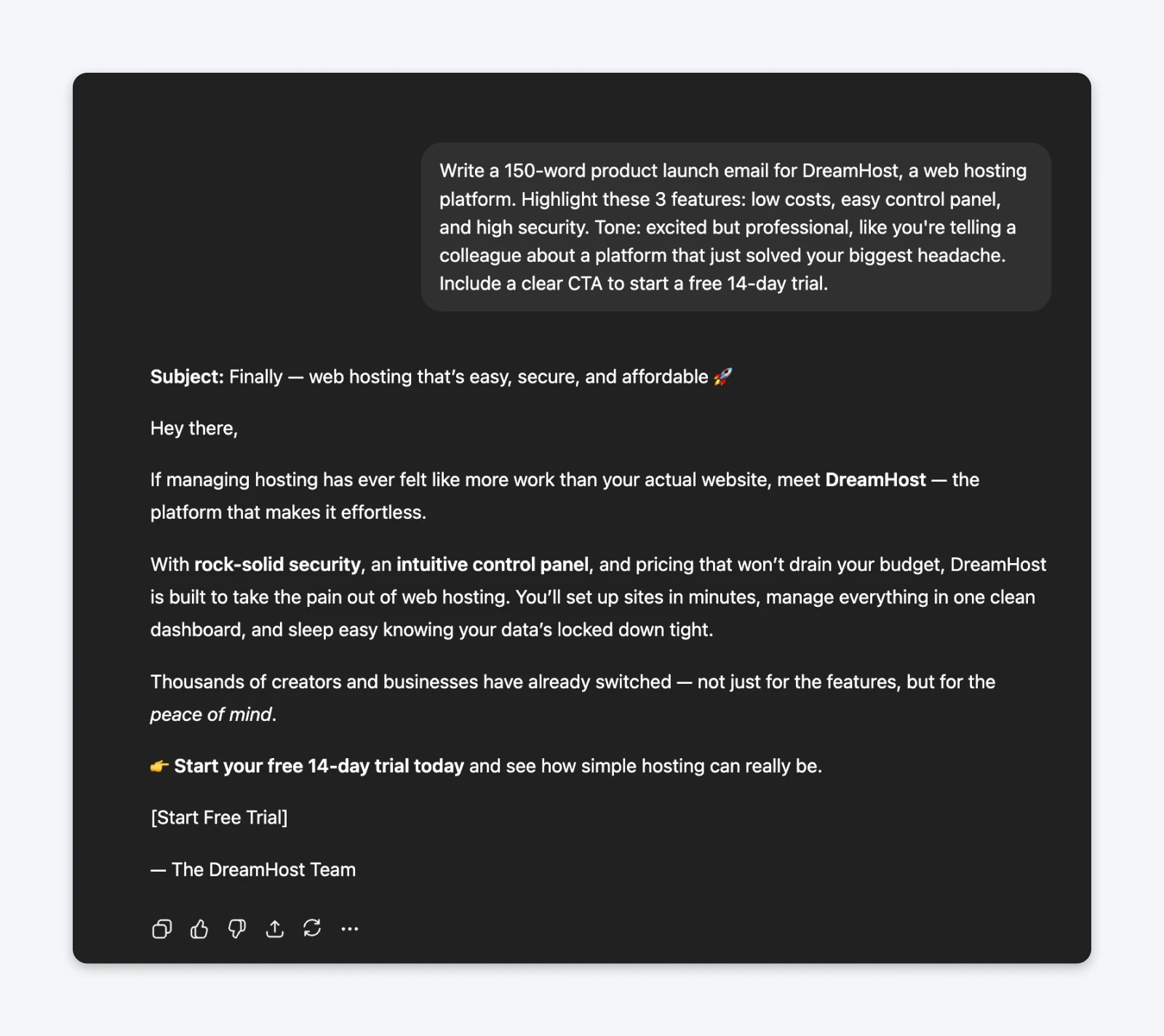
The prompt (specific):Write a 150-word product launch email for DreamHost, a web hosting platform. Highlight these 3 features: low costs, easy control panel, and high security. Tone: excited but professional, like you’re telling a colleague about a platform that just solved your biggest headache. Include a clear CTA to start a free 14-day trial.
- The vague prompt produced something so generic it could have described literally any productivity tool.
- The specific prompt generated copy with personality, concrete benefits, and actual detail about features.
Why it works: ChatGPT operates on pattern matching. When you provide specific constraints (word count, audience size, three exact features, tone comparison), it has clear parameters to work within. Specificity eliminates ambiguity.
2. Role Assignment (9/10)
Starting prompts with “You are a [specific role]” taps into ChatGPT’s training on professional writing patterns. The model has learned associations between roles and writing styles, so explicitly naming expertise improves output quality for creative and professional tasks.
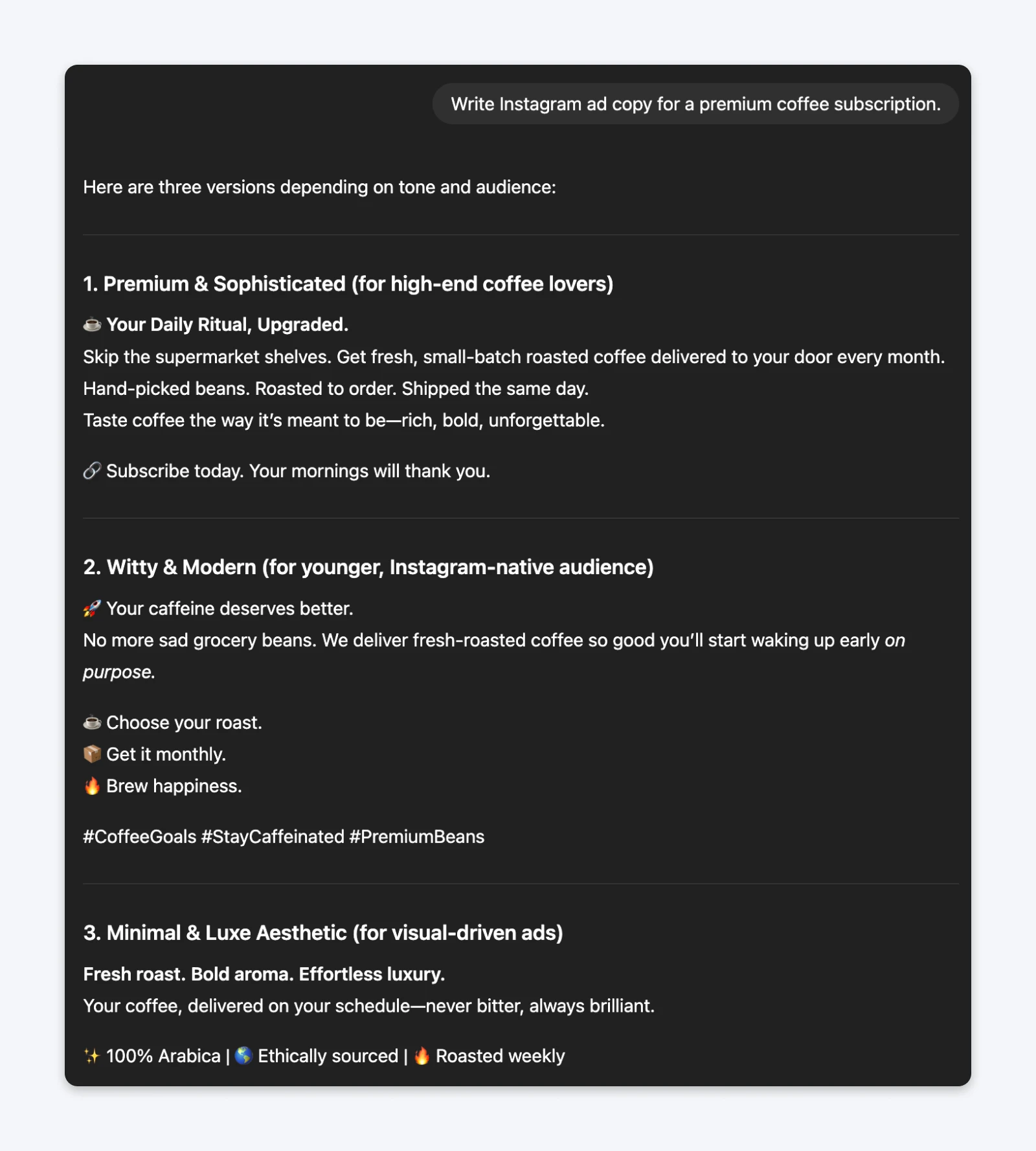
The prompt (without role):Write Instagram ad copy for a premium coffee subscription.
The prompt (with role):You are an experienced direct-response copywriter who specializes in Instagram ads for premium lifestyle brands. Write 3 versions of ad copy (each under 125 characters) for a premium coffee subscription service that emphasizes small-batch roasting and direct trade relationships.
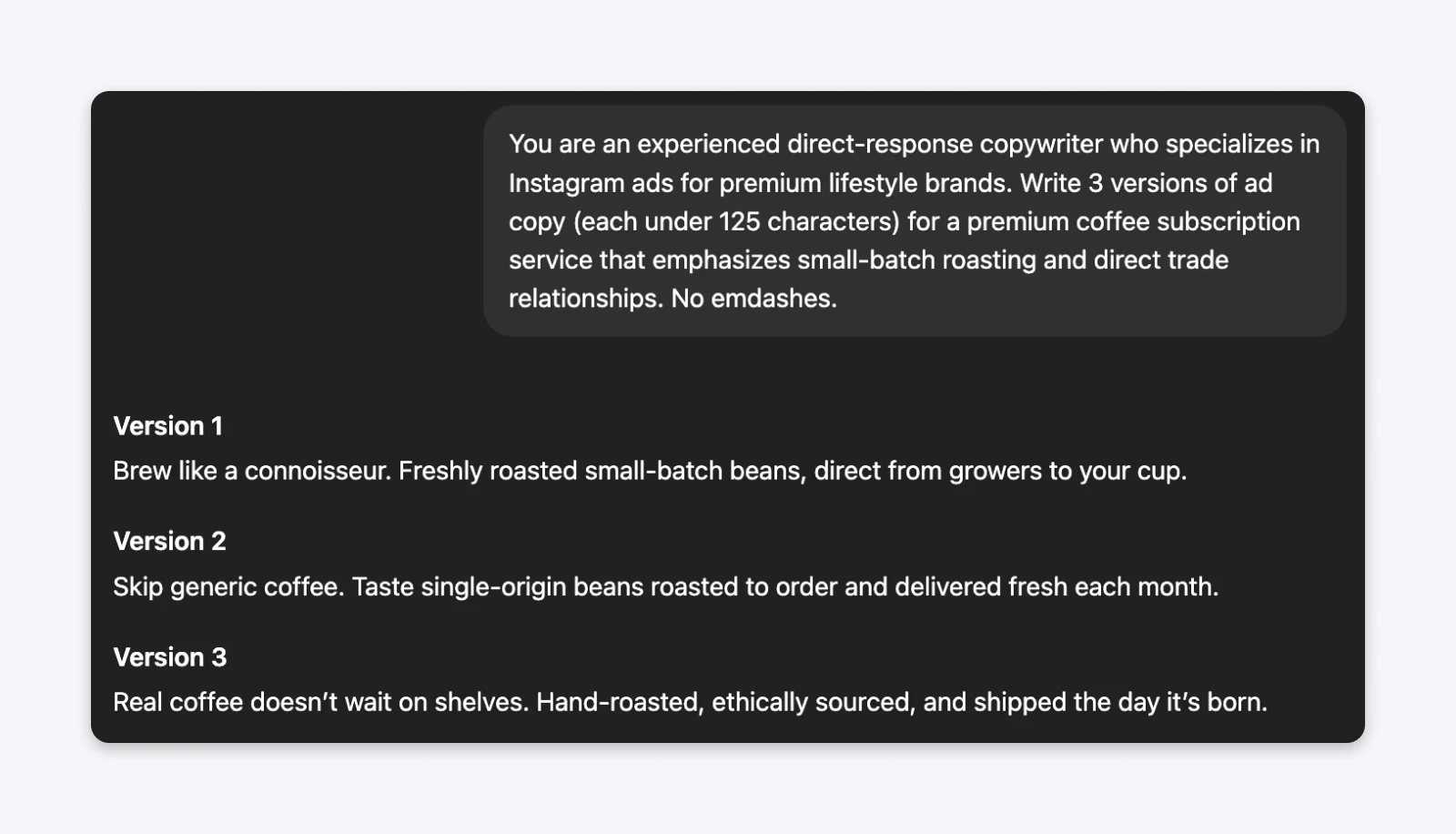
The role-based prompt generated copy that understood direct-response principles: leading with hooks, focusing on specific benefits, and using persuasive structure. The generic prompt produced enthusiasm without a strategy.
Why it works: ChatGPT’s training includes countless examples of professional writing from specific roles. Invoking “direct-response copywriter,” for instance, lets the model match patterns associated with that expertise rather than generic marketing writing.
3. Provide Concrete Examples (a.k.a. Few-Shot Learning): 9/10
This is a well-documented technique for language model fine-tuning, and it’s quite simple to implement.
You provide the input in terms of what you want and give examples of the outputs. What happens with this setup is that the model understands the patterns that you are expecting from the outputs and tries to emulate them as closely to your examples as possible.
So, you end up reducing the back and forth required to get the desired results and start getting consistently good results.
The prompt (without examples):Write a professional response to a customer requesting a refund due to shipping delays.
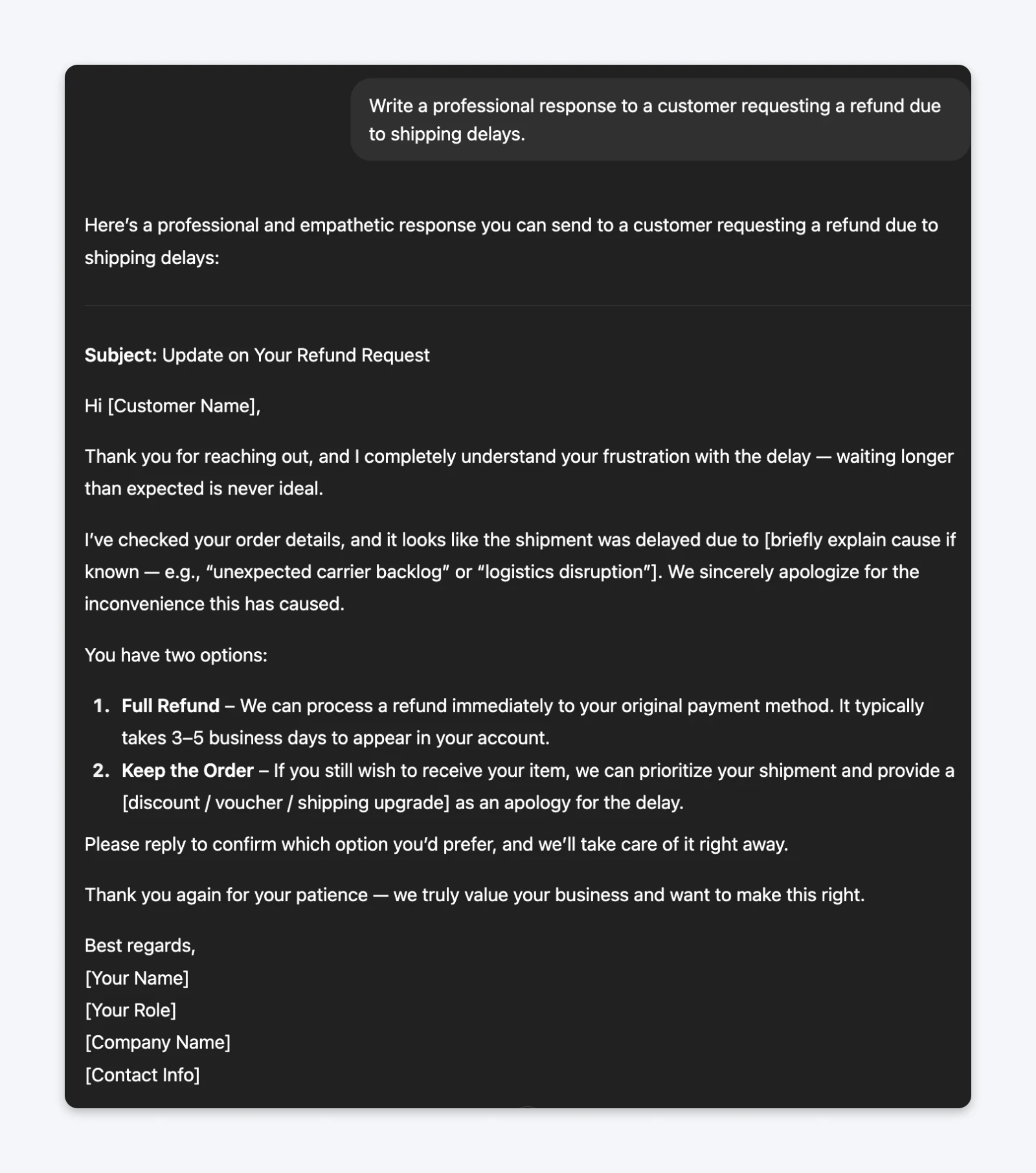
The prompt (with examples):Write a response to a customer requesting a refund due to shipping delays. Here are two examples of our brand voice in support emails:Example 1: “Hey Sarah, I’m so sorry your order got caught in transit limbo. That’s incredibly frustrating, especially when you’re excited about trying new gear. I’ve processed a full refund to your original payment method.You should see it within 2-3 business days. I’m also sending a replacement order with expedited shipping at no charge. You shouldn’t have to choose between a refund and getting what you ordered.”
Example 2: “I completely understand your frustration, Marcus.Shipping delays are the worst, and we dropped the ball on communication here. Let’s fix this right now: I’m issuing your refund today and including a $25 credit for your next order. No more hoops to jump through. You should see it in your account right now.”Match this voice exactly and format the output as an email.
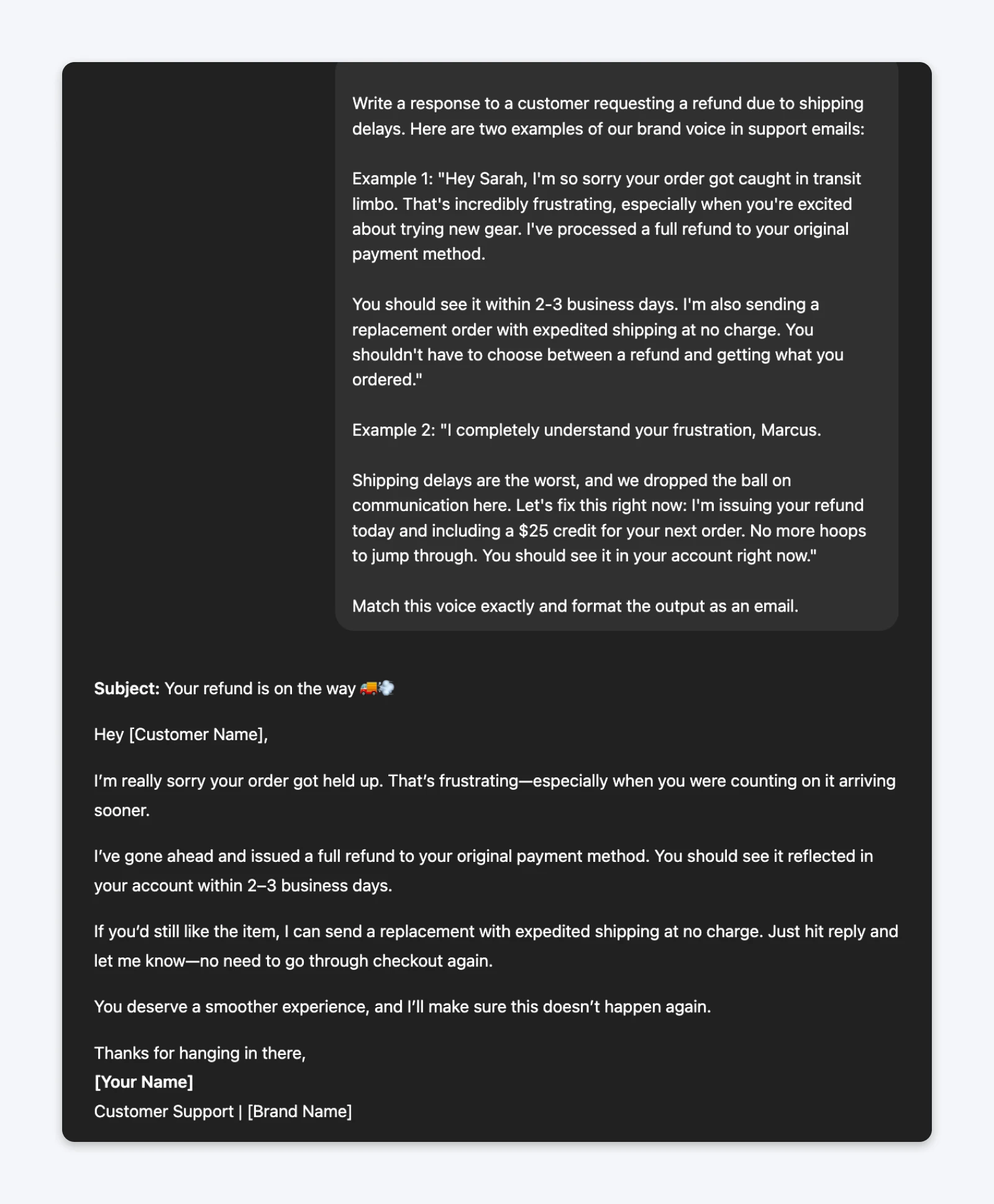
The example-based prompt generated a response that matched my expected brand voice: empathetic without being syrupy, solution-focused without being defensive, and genuinely helpful without corporate language.
Why it works: ChatGPT learns from the patterns in your prompted examples better than giving it a paragraph of writing style instructions. That includes sentence structure, vocabulary choices, how you balance empathy with action, and what you emphasize. Two quality examples teach more about your voice than a paragraph describing your tone.
4. Specify Output Format Precisely: 8/10
Telling ChatGPT exactly how to structure output saves massive formatting time. This technique is particularly valuable when you’re pasting content directly into other tools, like your content management system (CMS), or need specific data structures.
The prompt (without format specification):Compare our app’s features to competitors.

The prompt (with format specifications):Create a well-researched comparison table with 4 columns: Feature Name, Our App, Competitor A, Competitor B. Include 5 key features. Use this exact markdown format:| Feature | Our App | Competitor A | Competitor B ||———|———|————–|————–|| [feature] | [details] | [details] | [details] |

The format-specified prompt generated a perfectly structured table I could paste directly into documentation—zero formatting time required. The generic prompt gave me with information in paragraph form, which required 10-15 minutes of manual table creation.
⚠️ Remember that the information in the table (and even the paragraph above) may be factually incorrect. In fact, every output should be checked for accuracy.
Why it works: ChatGPT can output in virtually any format, but it defaults to prose unless its training model specifically associates certain words with certain formats (a case study would automatically have introduction, challenge, solution, and impact sections). Explicitly specifying structures, like tables, lists, specific markdown, JSON, etc., tells the model exactly how to organize the information.
5. Tell GPT What NOT To Do: 7/10
Large language models (LLMs), including ChatGPT, have repetitive writing patterns. People who use them long enough can recognize the same patterns from a mile away. So, if you’re using ChatGPT to write marketing material, make sure the output does not sound like AI slop.
You need it to be fun, interesting, and have a personality. You can tell it exactly what you want to avoid (specific words, phrasings, or structures), and it generally sticks to the rules. For longer content, however, these rules may end up broken.
The prompt (without constraints):Write a product description for a premium coffee subscription.
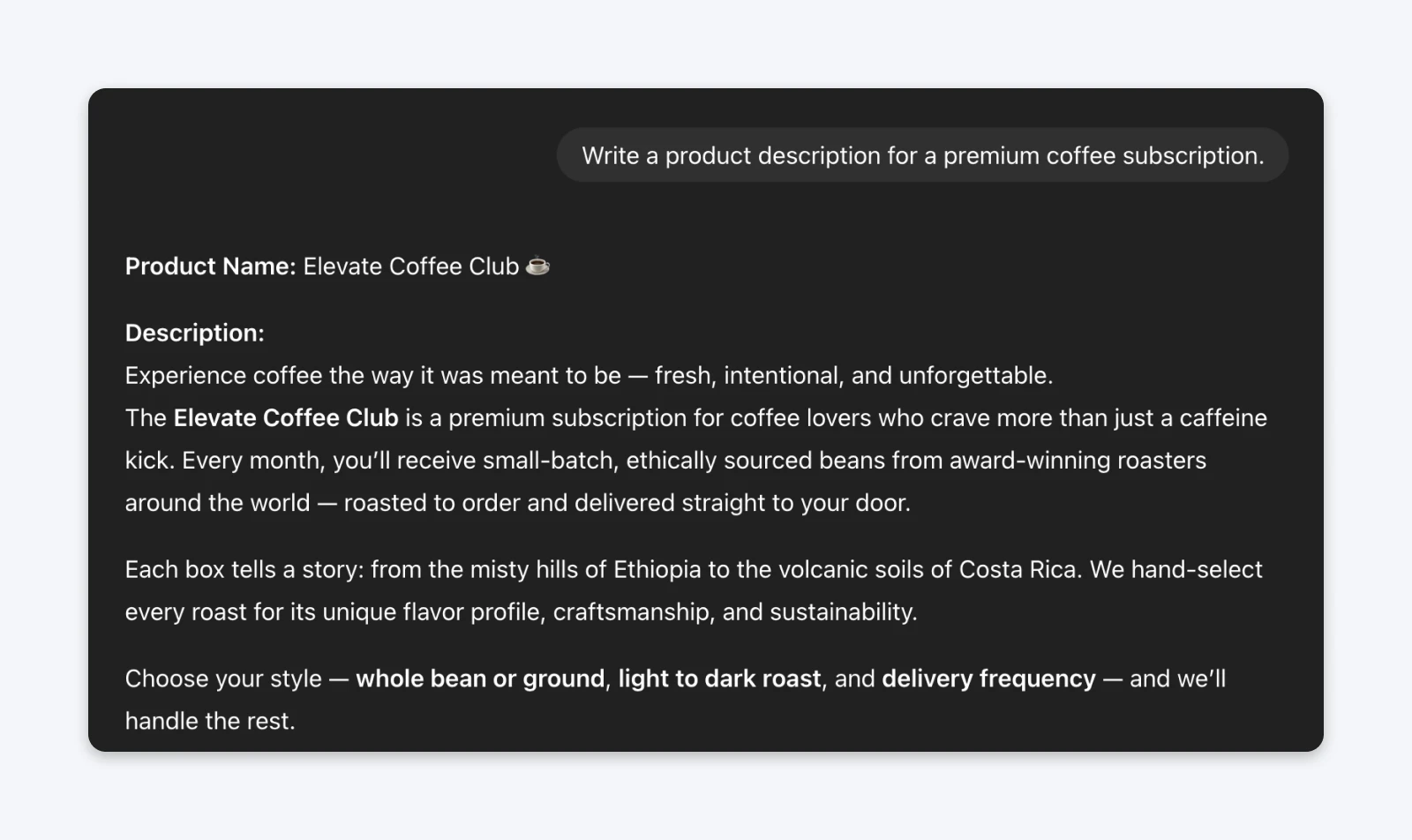
The prompt (with negative constraints):Write a product description for a premium coffee subscription.DO NOT use these words or phrases: artisanal, curated, journey, experience, passionate, craft, elevate, hand-selected.DO NOT exceed 75 words.DO NOT use exclamation points.Focus on: specific sourcing details, what makes the coffee actually different, and concrete benefits to the customer. No em dashes.
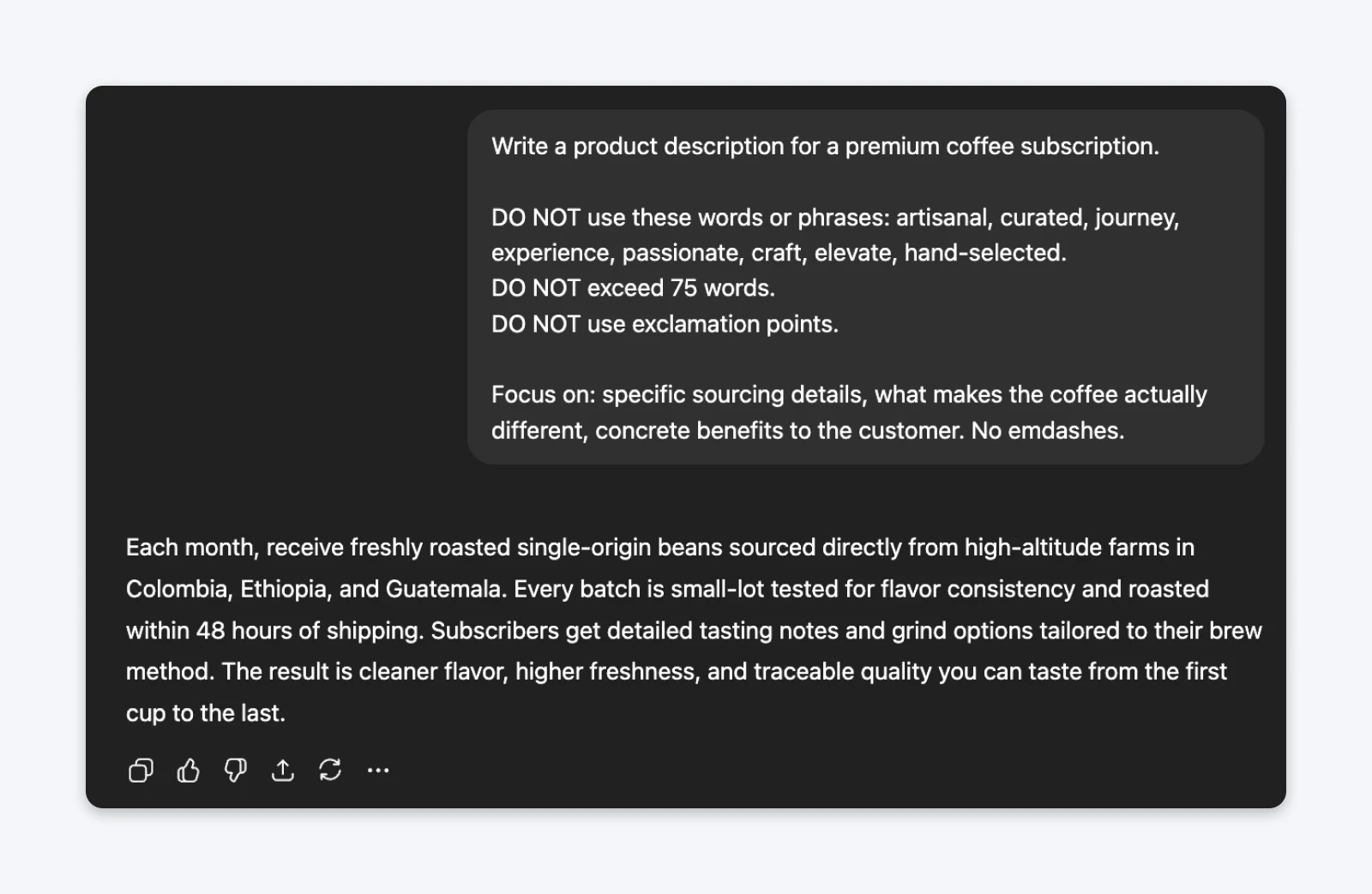
Notice the output from the first prompt has a lot of em dashes and sounds a bit salesy. I do think my ChatGPT has become neutral due to all the memories from my previous chats. But I definitely like the second version as it follows my specific constraints.
Why it works: ChatGPT learns from patterns across the internet, which means it defaults to common phrasings. When those common phrasings are exactly what you dislike, negative constraints explicitly block those patterns and force alternative approaches.
6. Clear Instructions First, Context Second: 7/10
Google’s AI prompting guide clearly suggests providing clear instructions about the task first and then providing context about the same.
Here’s the snippet from the guide:

LLMs prioritize information sequentially (the first sentence gets the highest priority). So, adding the task first gives the LLM enough information to perform the task. The context can be included as part of the prompt later.
The prompt (context-first):We’re a SaaS company targeting remote teams of 10-50 people. We’ve been in business for 3 years and recently launched a new feature for AI-powered task prioritization that analyzes team workload and suggests optimal task sequencing. Our main competitors are Asana and Monday.com, but we differentiate through deeper AI integration and better Slack connectivity. Our target customers are typically tech-savvy project managers who are frustrated with manual task organization. We need an announcement email for this new feature.
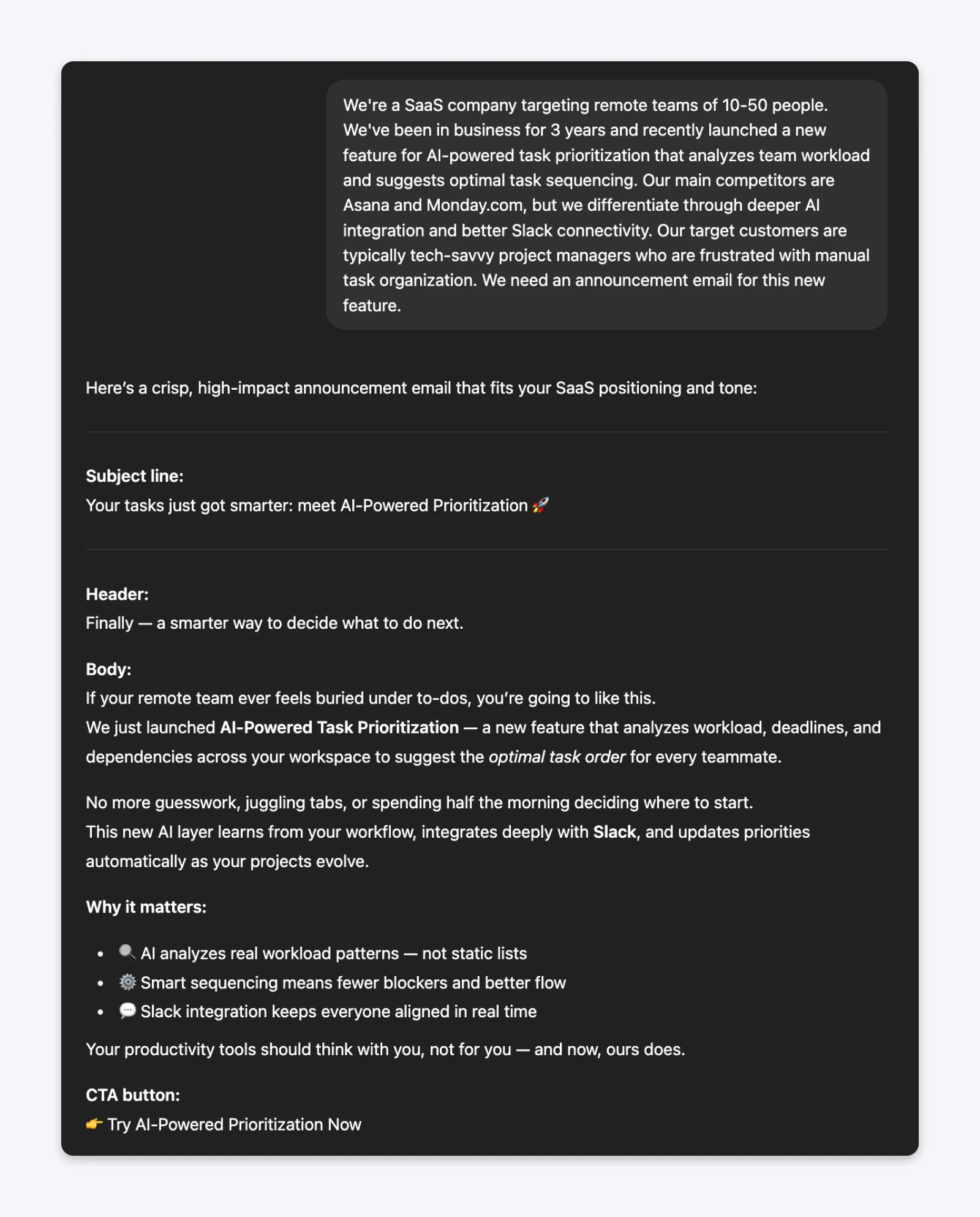
The prompt (task-first):Write a 200-word product announcement email for our new AI task prioritization feature.Context: We’re a 3-year-old SaaS company targeting remote teams (10-50 people). Main competitors: Asana and Monday.com. Our differentiation: deeper AI integration and native Slack connectivity. Target audience: tech-savvy project managers frustrated with manual task organization.Emphasize: how AI sequencing saves time and reduces overwhelm.
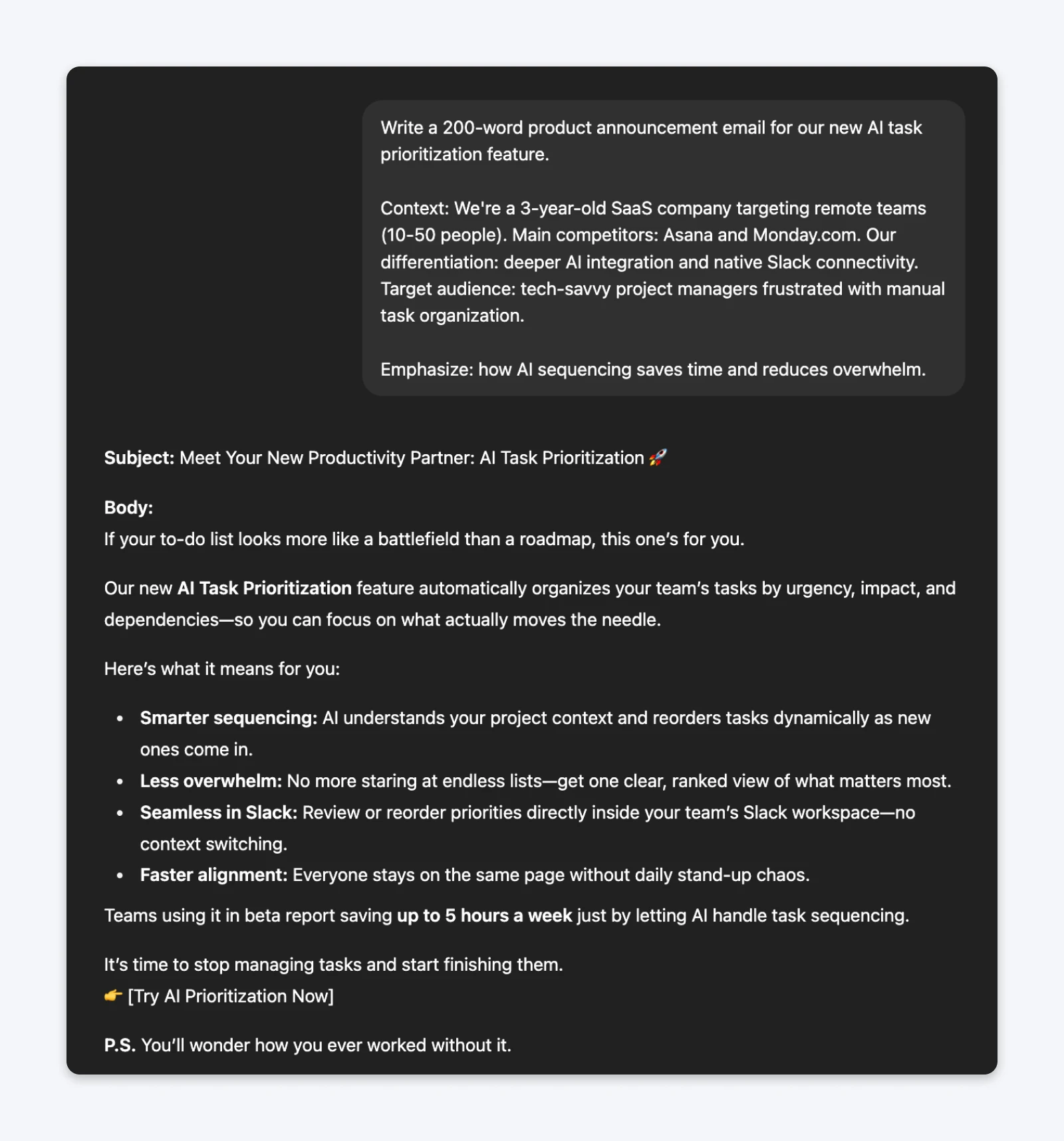
This technique has become less important as LLMs have become smarter. But considering that companies are suggesting prompts to be in this structure, they’re likely using that same structure for their model fine-tuning. And as you go deeper into prompt engineering, these fundamentals can help get consistent results.
Why it works: Starting with the task establishes the goal immediately, then context informs how to approach that goal. Context-first structure can muddy what you’re actually asking for, especially in longer prompts.
7. Use Step-by-Step Numbered Instructions: 7/10
Use numbered lists for multiple items. For example, if you want GPT to create 15 social media posts, 1 blog post, and 10-12 hashtags, it’s likely the language model will fail to provide everything at once.
The prompt (without steps):Create social media content for our app launch, including tweets, a LinkedIn post, hashtags, and posting time recommendations.

The Prompt (with numbered steps):Create social media content for our app launch:1. Write 3 tweet variations (under 280 characters each, include hook and CTA)2. Write 1 LinkedIn post (150-200 words, professional tone emphasizing ROI)3. Create 5 relevant hashtags for Twitter and 5 for LinkedIn4. Suggest optimal posting times for the tech industry B2B audience5. For each post, explain the messaging angle chosenDeliver each component clearly labeled.
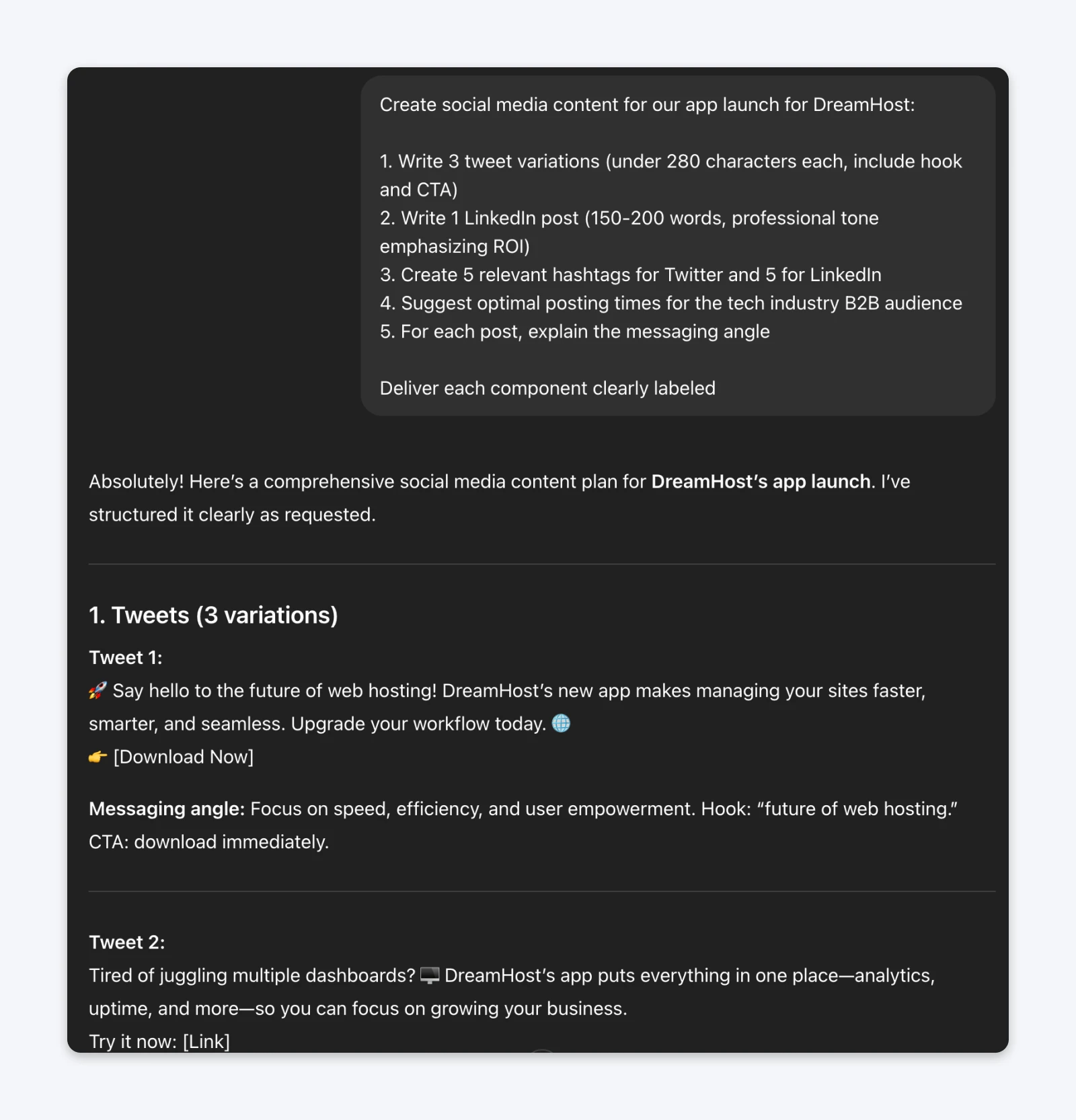
The above outputs aren’t the best representations since we have very few items in the list. However, you’ll begin to notice real differences when the number of items or tasks per list item begins to increase.
Why it works: These numbered instructions create a clear checklist in the “mind” of ChatGPT that can easily be followed sequentially.
8. Ask “Do You Have Any Questions?”: 6/10
Ask the model to ask you clarifying questions. You get help filling in the knowledge gaps you assumed were unnecessary and helping you add more relevant context to your outputs.
But the jump in output quality is only visible if the topic is a little “general” and you answer the questions with data and specificity.
The prompt:Create a comprehensive onboarding email sequence for new users of our project management app. Do you have any questions before you begin?
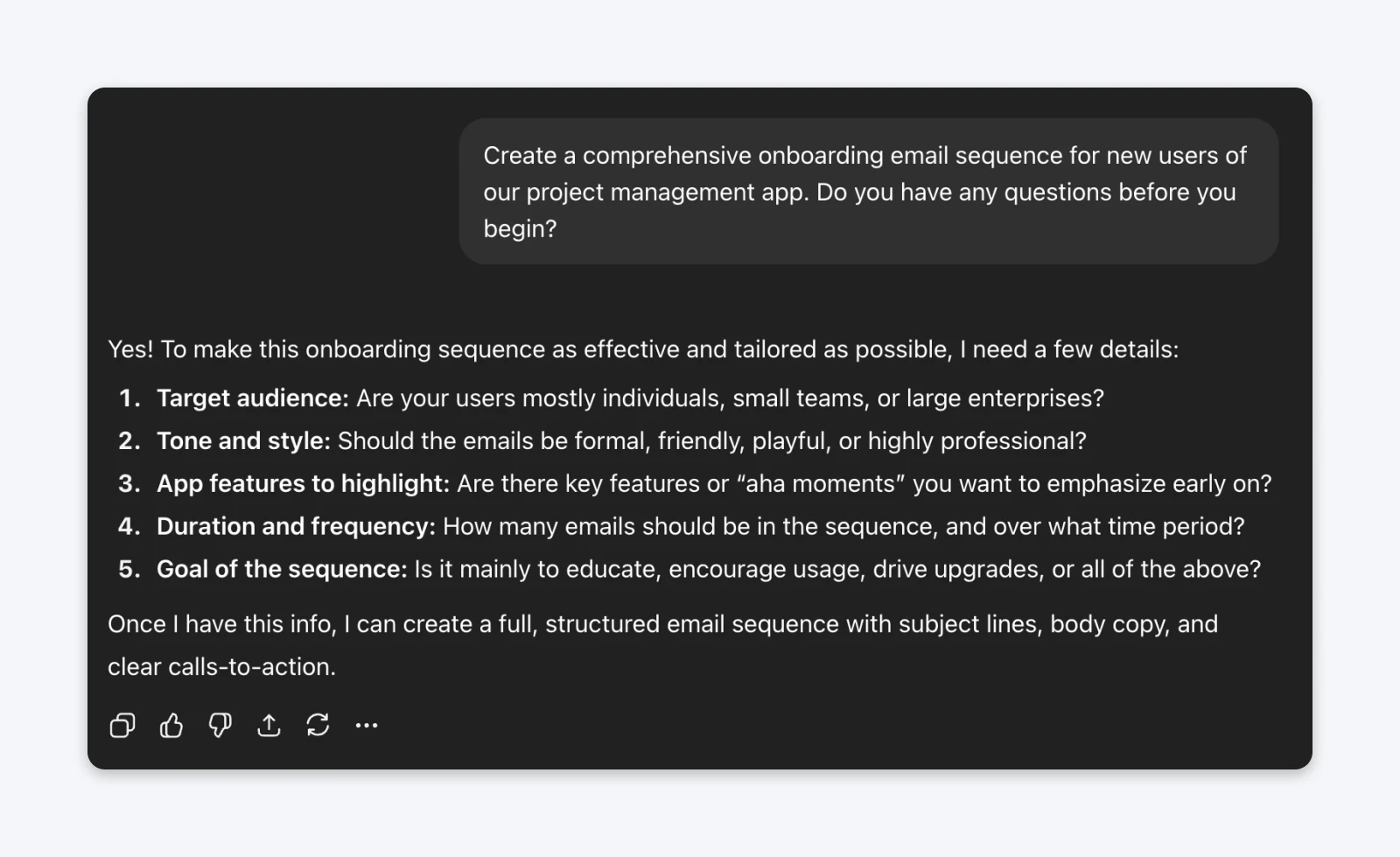
From my testing with ChatGPT, the results were inconsistent. Sometimes ChatGPT generates genuinely helpful questions about the target audience, email frequency, or specific features to emphasize.
For highly niche industries, the questions start to sound vague, and they become more and more irrelevant the deeper you go into a subject.
Why it works (sometimes): If you’re working on a topic you don’t have much information about, ChatGPT can fill in the knowledge gaps and add important context. It can sometimes help us discover what we didn’t know we didn’t know.
9. Chain of Thought (“Think Step-by-Step”): 6/10
Adding phrases like “think step by step” or “explain your reasoning” makes ChatGPT show its work — even when not in thinking mode or when the LLM doesn’t support thinking. This technique improves outputs for analytical tasks but adds unnecessary length to creative work.
The prompt (without chain of thought):Analyze why our email open rates dropped 15% last month and recommend solutions.
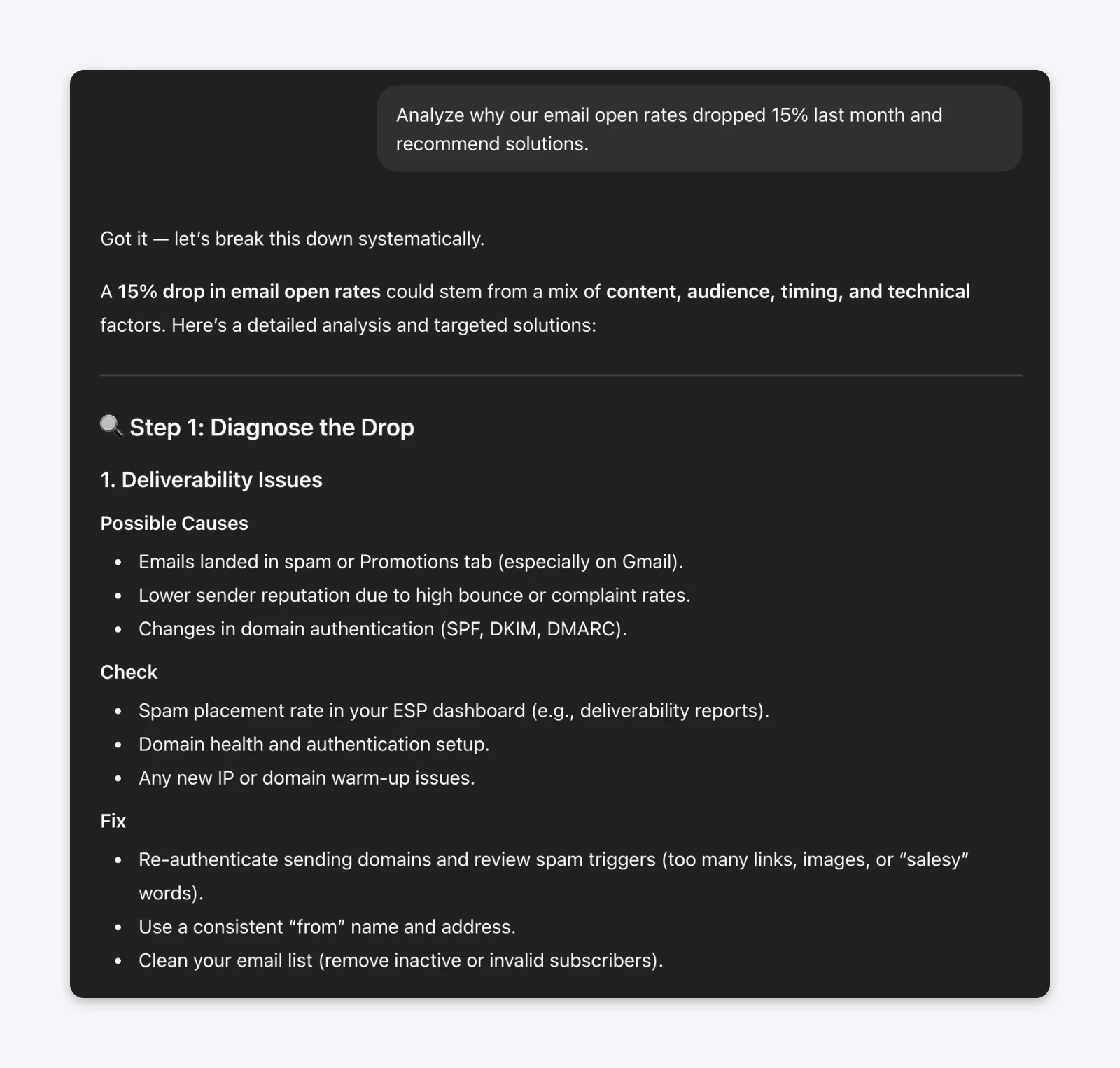
The prompt (with chain of thought):Analyze why our email open rates dropped 15% last month and recommend solutions. Think through this step by step, showing your reasoning for each potential cause before making recommendations.
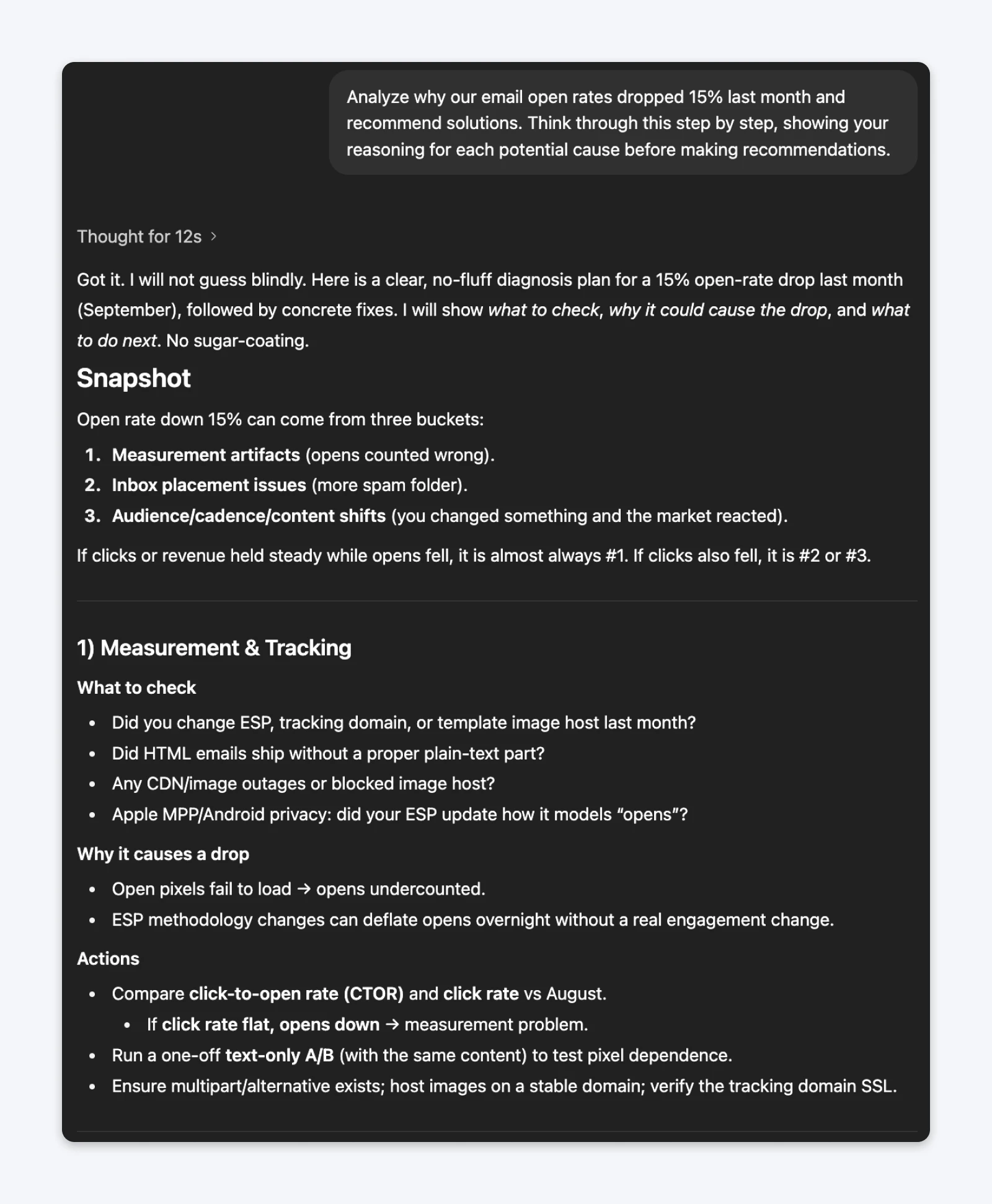
Without adding context to the data from your analytics dashboard, the responses with or without chain-of-thought are going to be generic. However, you’ll notice that GPT5 decided to invoke thinking mode to reason through the problem when given the chain of thought prompt.
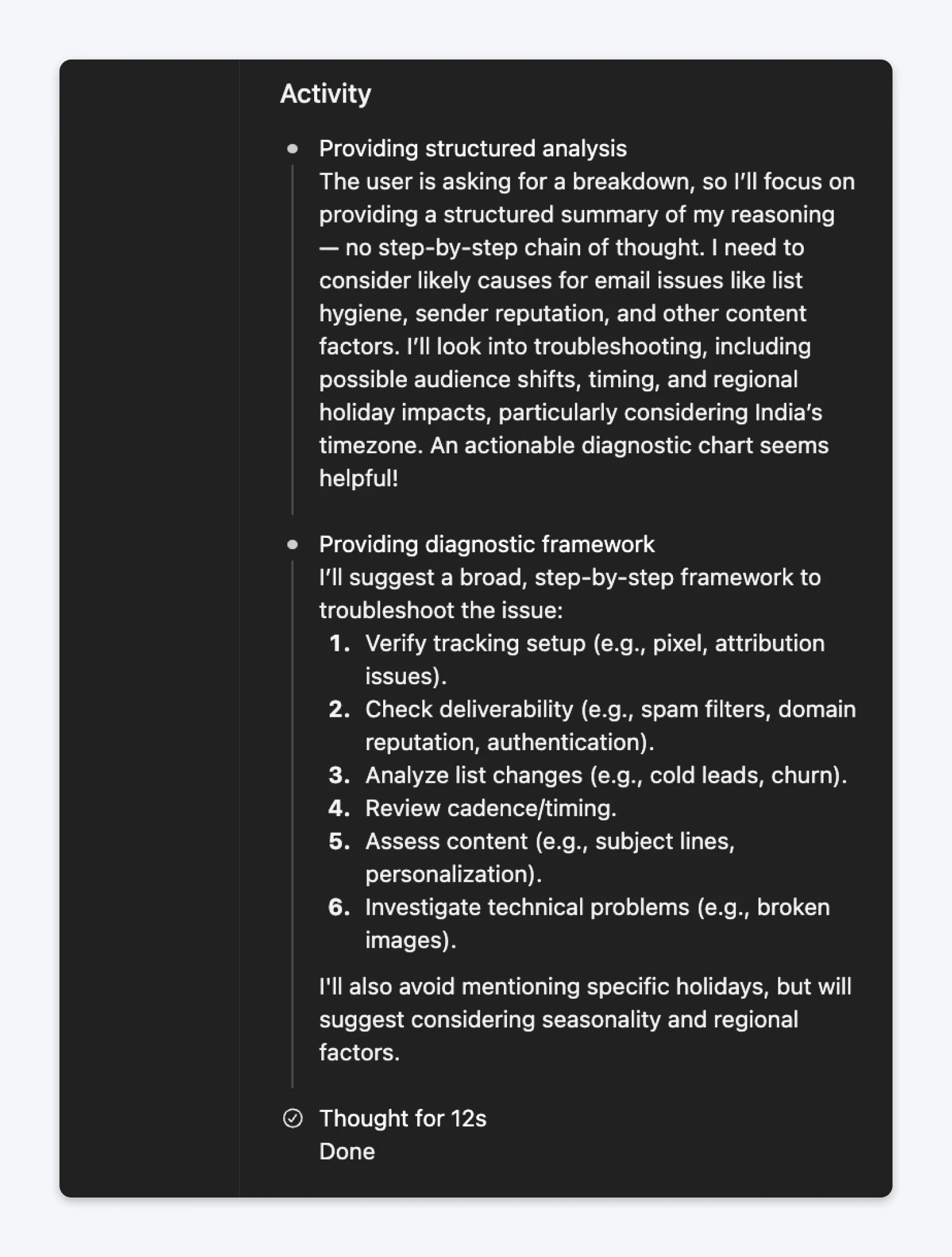
The thinking clearly shows that it went through the step-by-step process to understand the problem and used that to respond. Compare that to the non-CoT prompt, and the response was quick and did not require thinking.
Why it works: If you’re working on analytical and problem-solving tasks, asking for reasoning helps you verify that the language model is going through the steps as you would. For creative tasks, like marketing copy, this may not be as useful.
10. Show Your Edits Back to ChatGPT: 7/10
Similar to few-shot learning, ChatGPT learns from your messages in the chat. If you get an output from GPT that is close enough but not perfect, and you edit it to your liking, share it as your response. I do this quite frequently and have noticed a clear improvement in the responses up to a certain point.
The prompt (after receiving and editing AI-generated ad copy):Here’s what I ended up using after editing your draft:“DreamHost is a budget-friendly shared-hosting starting from ~$2.59/month and comes with a 97-day money-back guarantee.”I improved the sentence structure and made it flow better. Do the same for the rest of the column entries.

Within the same chat, you’re likely to get a great response, since the language model has picked up on the patterns that you like.
Fortunately, due to cross-chat referencing and internal memory, ChatGPT is also able to reference your previous conversations to provide much better outputs from the first time.
Why it works: ChatGPT maintains a persistent memory of your preferences across conversations. The effort required to share edits doesn’t match the limited payoff. You’re better off creating comprehensive examples upfront (Technique #3).
11. Use Clear Delimiters to Separate Instructions from Content: 6/10
When your prompt includes both instructions and content to process (like examples, text to analyze, or customer feedback), use delimiters to distinguish between the two.
This prevents ChatGPT from confusing your instructions with the content itself.
The prompt (with delimiters):Rewrite the customer email below to match our professional support voice.—EMAIL TO REWRITE—Hey thanks for reaching out about the bug. Yeah we know about it and someone’s looking at it. Should be fixed soon probably. Let me know if you need anything else.—END EMAIL—
Requirements:– Maintain warmth while being professional– Provide specific timeline– Include clear next steps
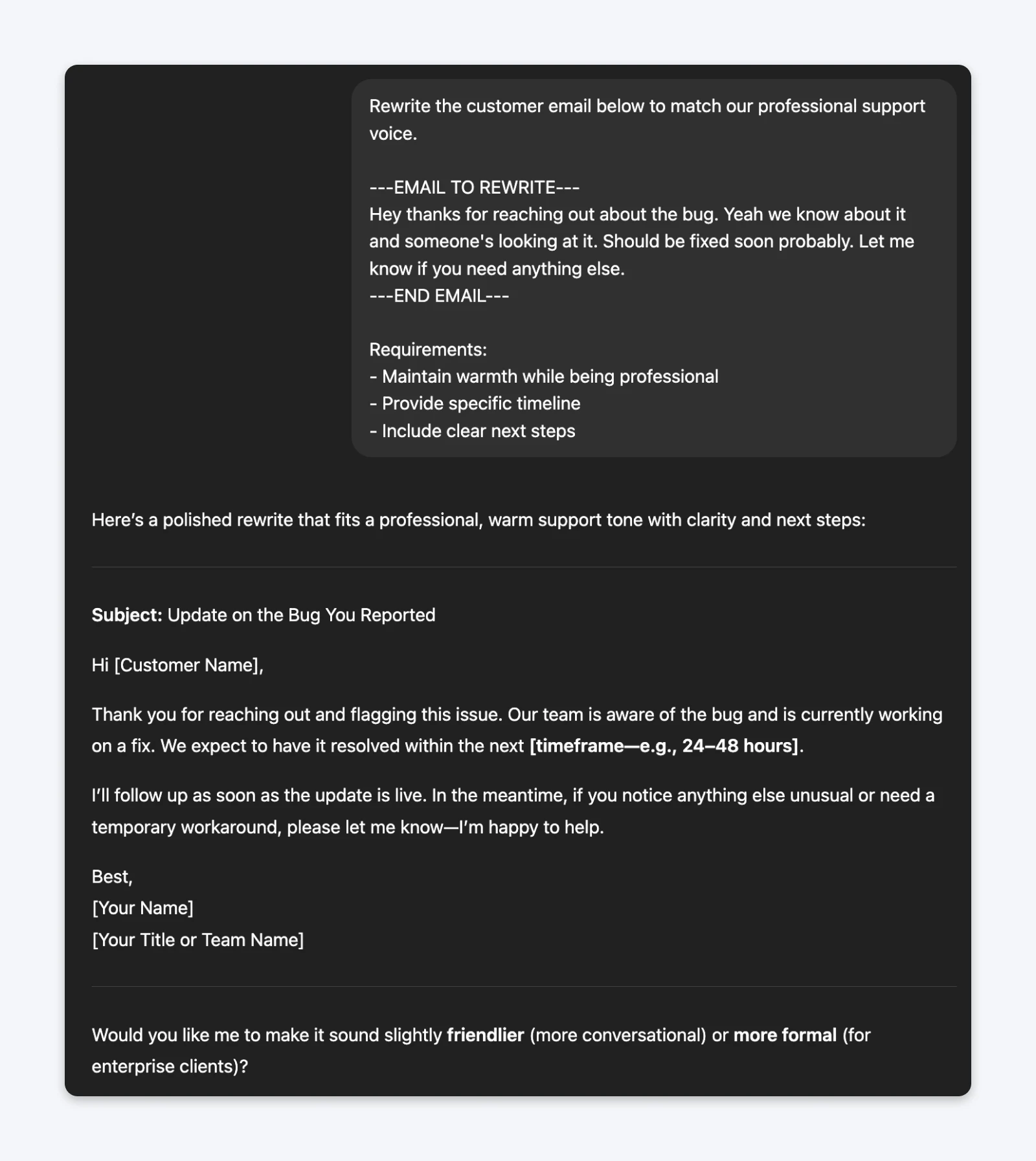
Delimited prompts consistently produce cleaner outputs because ChatGPT can clearly understand what’s an instruction vs. what’s content. Without delimiters, especially in longer prompts, you’ll consistently see ChatGPT miss the prompted instructions.
Why it works: Delimiters (triple quotes, XML tags, markdown sections, or simple dashes) create explicit boundaries. This is particularly valuable when you’re providing multiple examples, analyzing customer feedback, or processing user-generated content where the language might resemble instructions. The technique becomes essential when your content includes phrases like “write,” “create,” or “analyze” that could confuse the model.
12. Avoid Being “Hard” on ChatGPT: 3/10
People used to suggest that demanding or critical feedback (“This is unacceptable, try again”) improves outputs.
But throughout my testing, it became clear that being demanding only makes ChatGPT redo the output. It’s unlikely to produce “better” outputs if it doesn’t know what better means.
The prompt (being “hard”):This response is terrible and completely missed the point. The tone is wrong, the structure is bad, and you didn’t emphasize what I asked for. Try again and do it right this time.

The prompt (being specific):This response needs revision:– Change tone from formal to conversational– Restructure to lead with the customer problem, not our solution– Emphasize the AI prioritization feature in the first paragraphPlease revise with these specific changes.
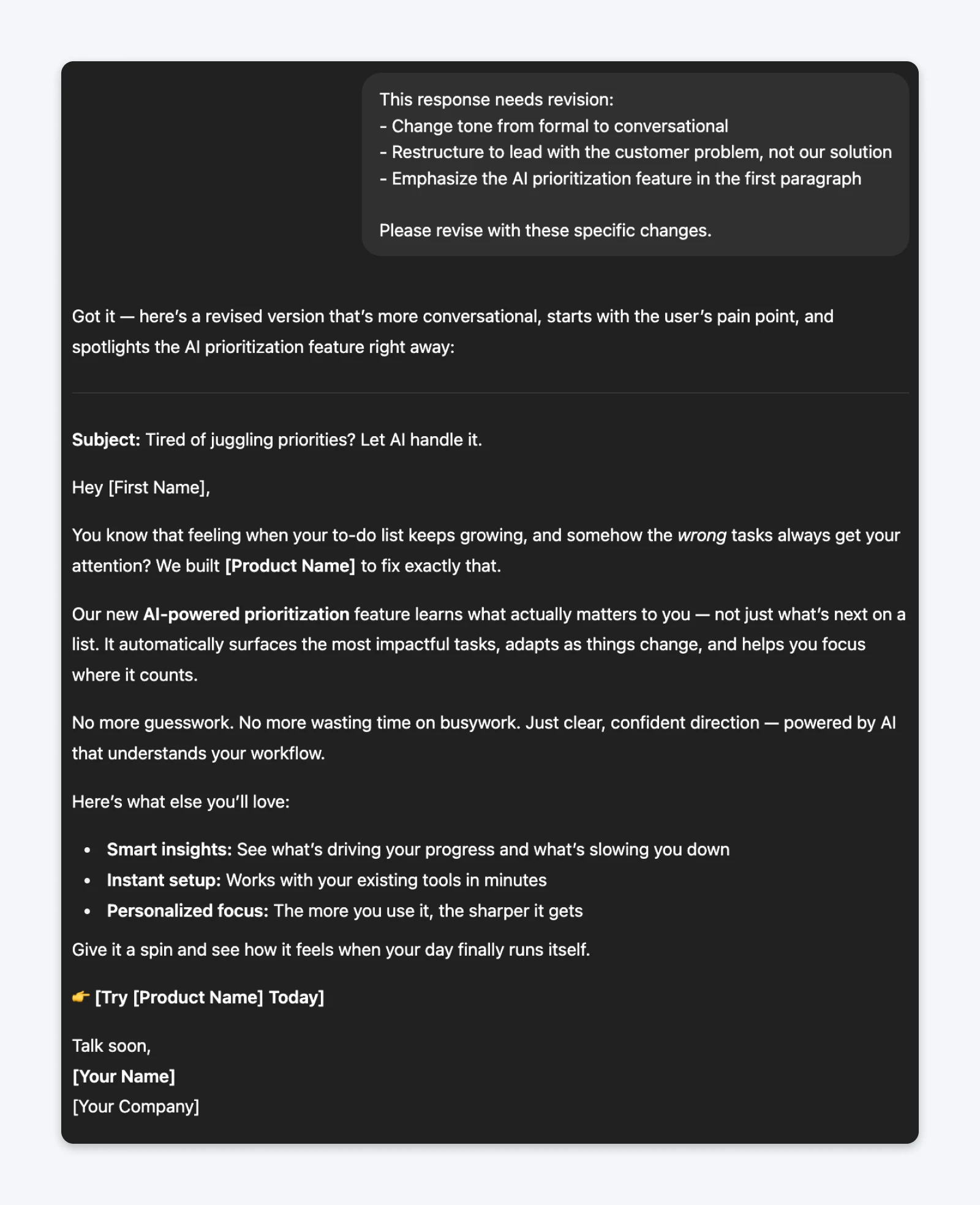
The “hard” prompt always produces a new output, maybe even forces ChatGPT to go into “thinking” mode. But the outputs are not consistently better. On the other hand, specific instructions on what you need to change will almost always yield you far better and cleaner outputs.
Why this “hack” persists: People confuse correlation with causation. When they get better results after being “demanding,” it’s usually because they’re being more specific about requirements in trying to be “upset,” not because ChatGPT responds to tone.
The 5 Core Techniques You Should Use
After testing a large variety of techniques (including these 12) across dozens of scenarios, the following five have consistently delivered results.
- Being ridiculously specific (10/10) is the foundation for everything else.
- Assigning a role (9/10) excels for creative and professional tasks.
- Providing concrete examples (9/10) maintains brand consistency.
- Specifying output format (8/10) saves formatting time.
- Telling ChatGPT what NOT to do (7/10) works when you know exactly what to avoid.
The remaining techniques offer situational value but aren’t core to effective prompting.
My Go-To Prompt Template
I have a couple of great templates lying around. But here’s one that has consistently delivered great results for almost every use case that I’ve thrown at it.
So use it for your experiments and see what kind of results you can get. Once you have a working prompt, the rest of your work becomes easy.
You are a [specific role with relevant expertise].Create: [Specific deliverable with word/character count]For: [Target audience with relevant details]About: [Topic/product with key information]Include:– [Specific required element 1]– [Specific required element 2]– [Specific required element 3]Format: [Exact structure needed]DO NOT:– [Specific thing to avoid 1]– [Specific thing to avoid 2]Example of our style:[Paste 1-2 relevant examples]
This framework works because it combines all the elements that produce consistently good results. You can always improvise, add more of the tips from the above 12 to see what fits best to the result you’re trying for.
Can You Create Thousand-Word Prompts?
Absolutely. The only limit is the prompt, and your expected output should not exceed the context window.
ChatGPT has a context window of 32k tokens per chat for the Plus and 128k tokens for the Pro version. Gemini has a context window of 2 million tokens per chat. Claude sits at 1 million.
Think of a token in a context window as part of a word.
32k tokens would translate to roughly 27k words. After this limit, ChatGPT forgets what was discussed before the most recent 32k tokens. Meaning the context “window” shifts.
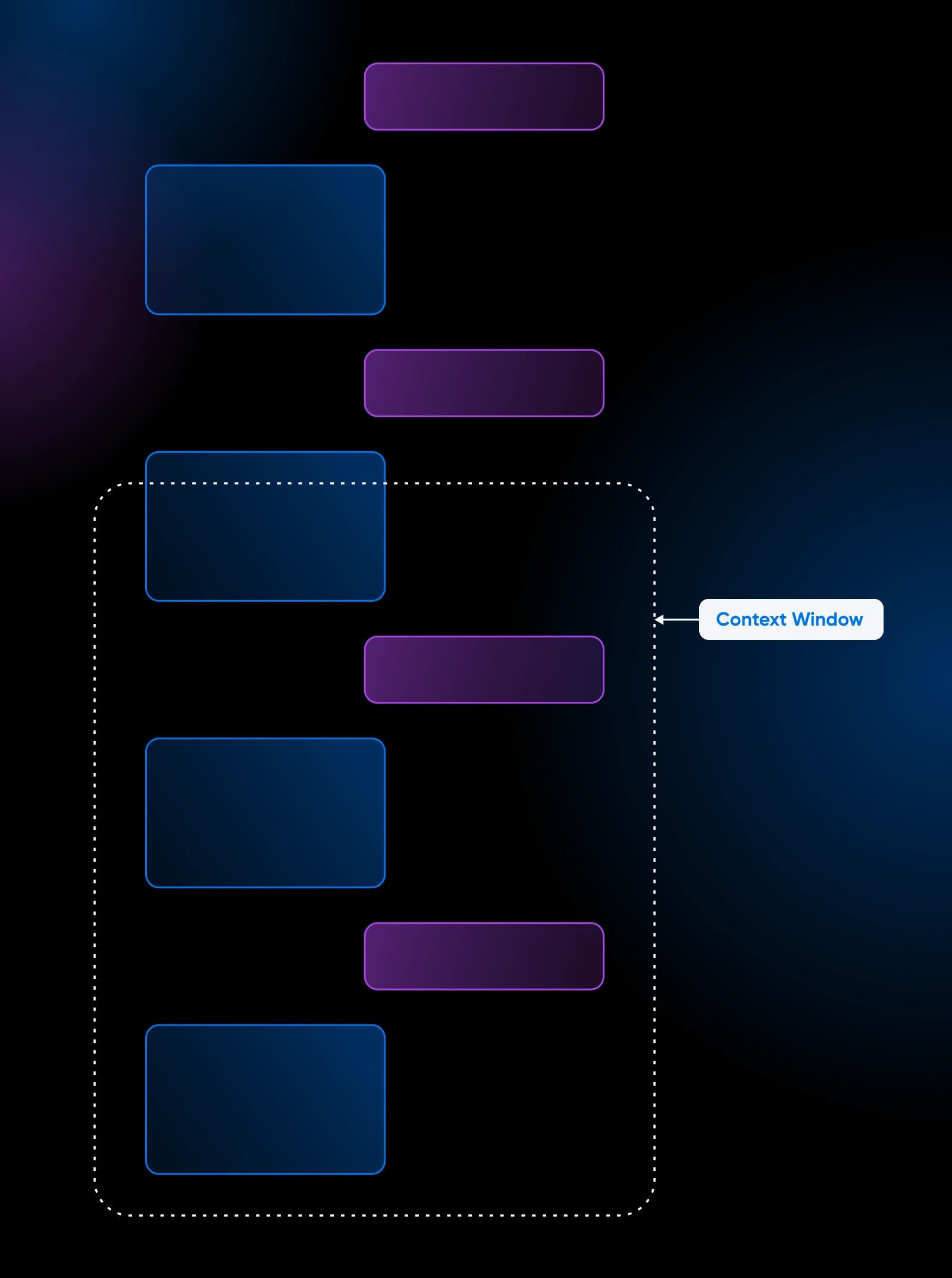
ChatGPT continues chatting with you even after the context window. But it will have no information about the chats beyond the context window.
If you notice ChatGPT starting to behave differently after a long conversation, try to reorient it by providing the original prompt once again, or start a new chat.
Consistent ChatGPT Prompting With “Projects”
LLMs don’t have context about your business, audience, and goals. They also do not know the constraints on output length, the format, the style, etc.
So, you can either provide context as part of your prompt every time you start a new chat or you can create a project in ChatGPT and add all of these as text files or markdown files.
Any new chats you start from inside the projects will have the required context by default.
1. Click Projects from the left sidebar.

2. Enter the project name and click Create project.
3. Click Add files to add all files you need for context.
What Next?
Prompt engineering isn’t a set-and-forget field. New models regularly break outputs you’d come to like on the previous models.
But the fundamentals of specificity, context, and examples remain constant. You only need to know which techniques solve which problems.
Focus on the five that matter and skip the gimmicks.
I’m currently experimenting with multi-step prompting sequences for complex content projects, prompt templates optimized by content type, and integration strategies with brand style guides. These are separate rabbit holes you can jump into.
But if you want to skip everything else and spend time on just one thing, spend it collecting great examples of what you want to achieve.
Everything else is optimization.
FAQs
What is prompt engineering for ChatGPT?
Prompt engineering is the practice of crafting specific, structured inputs to get better outputs from AI language models like ChatGPT. It involves techniques like providing detailed context, using role assignments, showing examples, and specifying exact format requirements to improve output quality and consistency.
Which prompt engineering techniques actually work?
These five techniques consistently deliver results: being ridiculously specific about deliverables, using role assignment for creative tasks, providing concrete examples of your desired output, specifying exact output formats, and explicitly stating what not to include.
Do I need to take a course on prompt engineering?
No. Most prompt engineering courses teach the same core principles available for free on the web. The real skill is in understanding which technique solves which problem for your specific use cases. I’d recommend applying the five core techniques I’ve outlined in this guide to your actual work and improving your prompts as required.
How specific should my ChatGPT prompts be?
Your prompts should include exact word counts, specific audience details, clear deliverables, and concrete constraints. Compare “write marketing copy” (too vague) with “write 150-word product email for remote teams highlighting 3 features: collaboration, AI prioritization, Slack integration” (appropriately specific).
Specificity eliminates ambiguity and dramatically improves output quality.
Does being demanding with ChatGPT improve outputs?
No. Testing shows attitude is irrelevant to output quality. When you need revisions, identify specifically what’s wrong (tone, structure, missing elements) rather than expressing frustration. Specificity helps; attitude doesn’t.
How long does it take to see results from better prompting?
Immediately. The difference between vague and specific prompts is visible in the first output. However, building your examples library and developing your personal prompt template takes 2-4 weeks of consistent practice to optimize for your specific use cases.



